In the world of industrial materials, wire mesh is widely used across various sectors for applications ranging from filtration to construction. Among the most popular types of wire mesh are woven wire mesh and welded wire mesh. While both materials serve similar purposes, such as providing structural integrity, security, and filtration, they differ significantly in their manufacturing processes, characteristics, and ideal applications. This essay will explore the key differences between woven wire mesh and welded wire mesh, helping to clarify which material is best suited for specific needs.

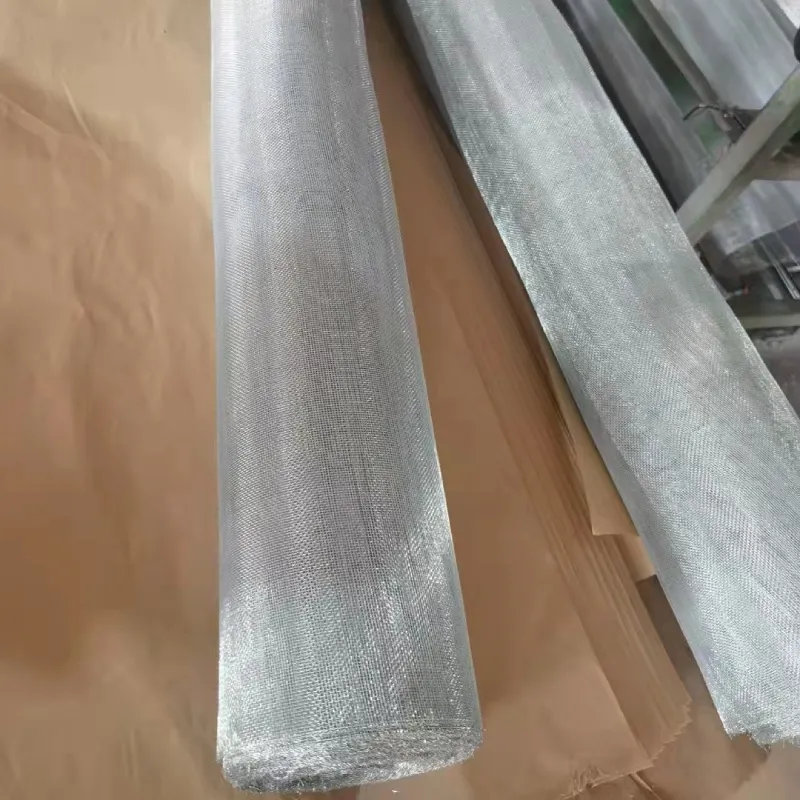
Manufacturing Process of Woven Wire Mesh
The primary distinction between woven wire mesh and welded wire mesh lies in how they are constructed. Woven wire is created by interlacing individual wires in a specific pattern, with the wires crossing each other over and under, much like a traditional woven fabric. The weaving process allows for flexibility in the type of weave, such as plain weave, twill weave, or dutch weave, giving designers a wide range of options for mesh density, strength, and application.
Strength and Flexibility of Woven Wire Mesh
When it comes to strength and flexibility, woven wire mesh and welded wire mesh serve different purposes. Woven wire is generally more flexible than welded wire because of its interlaced structure. This flexibility makes woven wire mesh ideal for applications where the material needs to adapt to changes in shape or load, such as in filtration systems or protective barriers. Woven wire mesh screens are particularly beneficial in applications requiring precise filtration, where flexibility allows the mesh to conform to varying pressures or fluid dynamics.
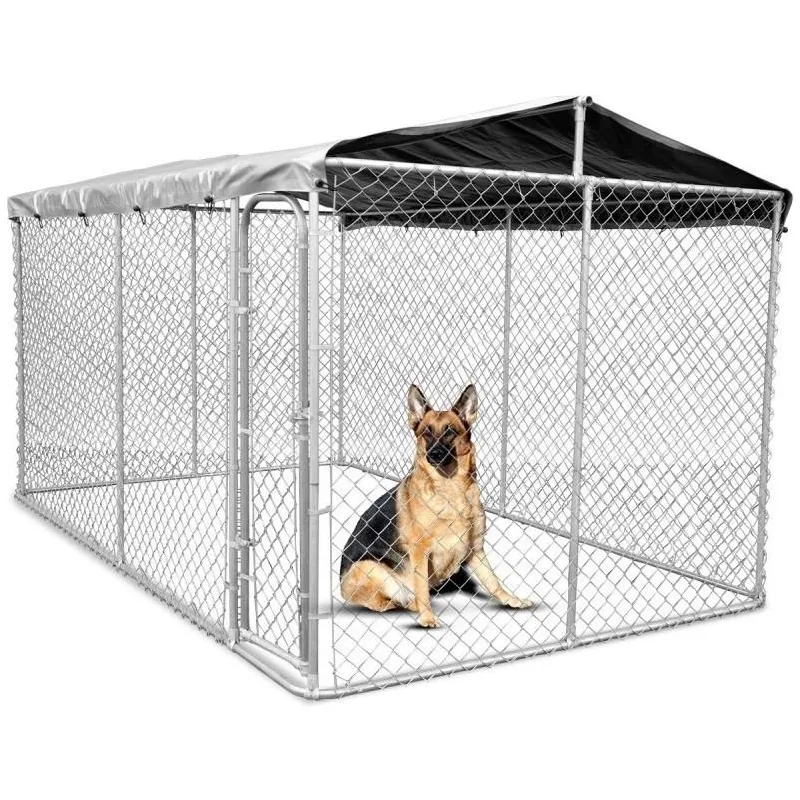
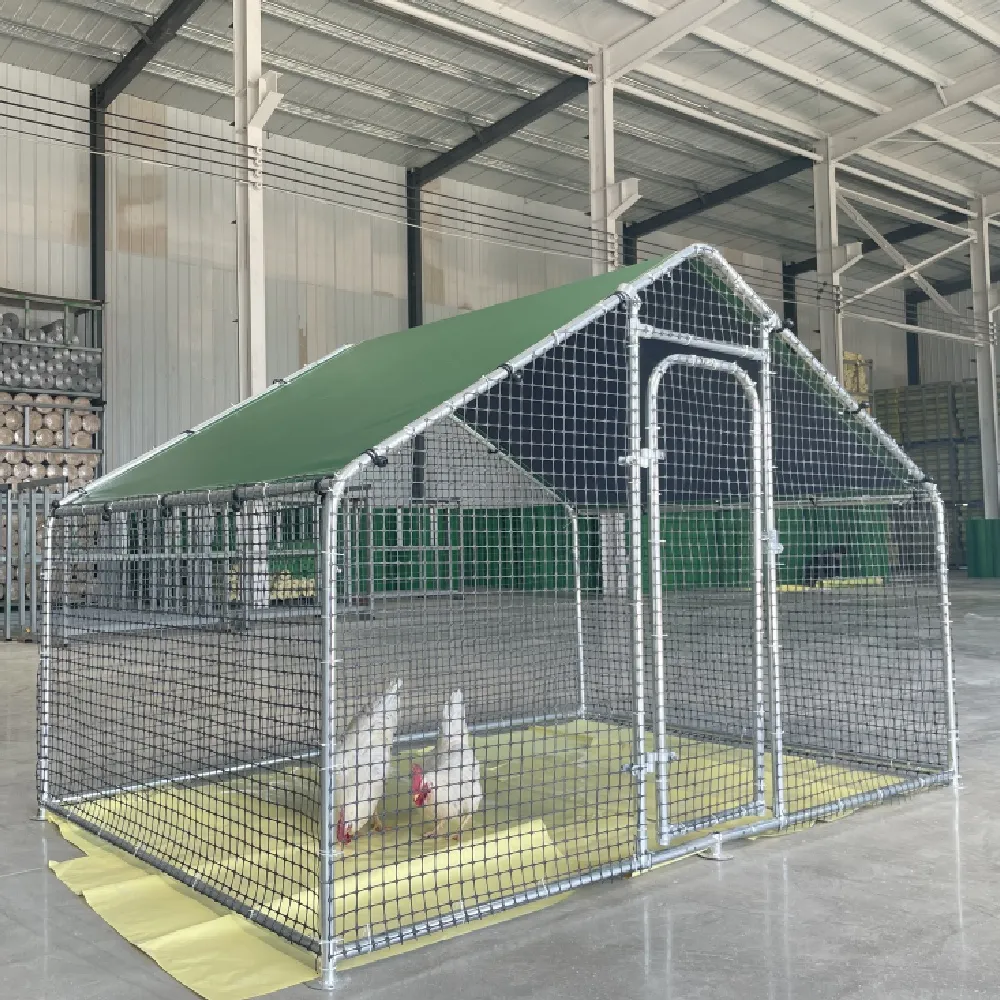
In contrast, welded wire mesh is significantly stronger and more rigid due to the welding process. It is often used in applications where structural integrity and strength are more critical, such as in concrete reinforcement, fencing, or heavy-duty security barriers. Welded wire mesh is less likely to deform under heavy loads, making it ideal for supporting concrete or other materials in construction.
Application Areas of Woven Wire Mesh
The differences in manufacturing and characteristics make woven wire mesh and welded wire mesh more suited for particular applications. Woven wire screen is often used in industries where precise filtration, flexibility, and adaptability are required. For example, woven wire screens are common in filtration systems for water treatment, oil refining, and pharmaceutical production. The fine and precise weave patterns allow for the filtration of various particle sizes, from fine sand and debris to microscopic contaminants. Additionally, woven mesh is commonly used in agriculture for crop protection and in architectural design for facades and ventilation systems, thanks to its aesthetic appeal and ability to handle dynamic stress.
Welded wire mesh, by contrast, is frequently employed in construction and security-related applications. Welded wire mesh is often used for fencing, concrete reinforcement, and creating rigid partitions or barriers. Its strength makes it ideal for applications that require a more rigid, fixed structure. It is often seen in road construction, animal enclosures, and security grids, where durability and resistance to bending or deformation are paramount.
Both woven wire mesh and welded wire mesh are valuable materials with unique strengths and ideal uses. Woven wire mesh excels in applications that require flexibility, precision, and adaptability, such as filtration and crop protection, while welded wire mesh is better suited for situations where strength and rigidity are paramount, such as in fencing and construction. Understanding the differences between these two types of mesh allows businesses and industries to make informed choices based on their specific needs, ensuring optimal performance and cost-effectiveness in their projects.