Galvanized Wire Material The Essential Guide
Galvanized wire material is a crucial component in various industrial applications, horticulture, and everyday construction tasks. Galvanization is the process where steel or iron wire is coated with a layer of zinc to protect it from corrosion. This treatment significantly enhances the material's durability, making it an excellent choice for a myriad of applications. In this article, we will explore the features, benefits, applications, and environmental impacts of galvanized wire.
Features of Galvanized Wire
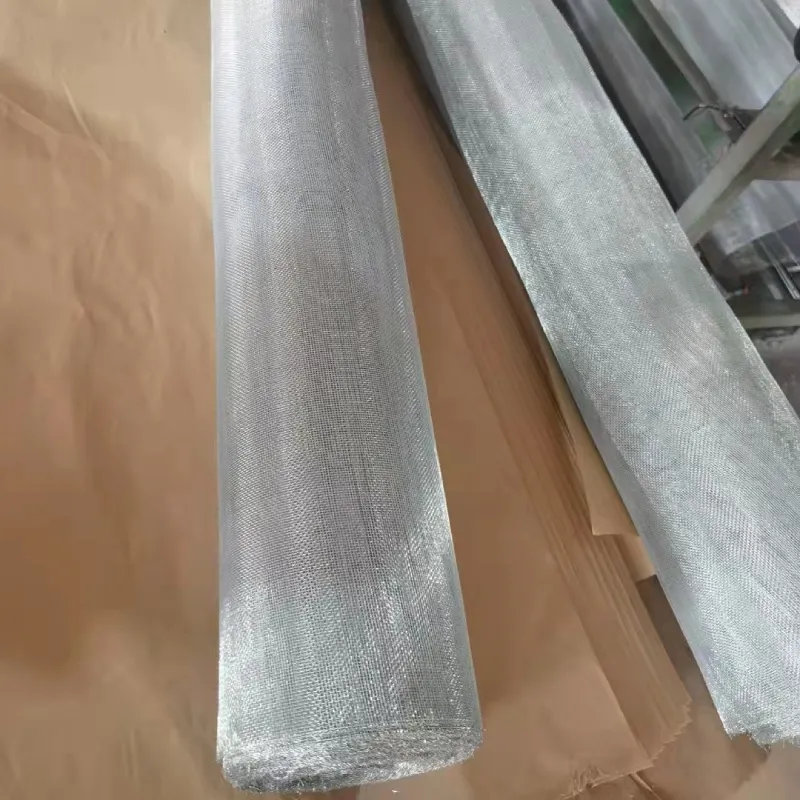
Galvanized wire is characterized by its shiny, metallic appearance and is available in various thicknesses and tensile strengths. The most common types of galvanized wire are either hot-dipped or electro-galvanized. Hot-dipped galvanized wire undergoes a process where the wire is submerged in molten zinc, creating a thick and robust protective layer. This method is typically more durable and suitable for outdoor applications. On the other hand, electro-galvanized wire is coated with a thinner layer of zinc through an electroplating process, making it more suitable for indoor use where exposure to harsh weather is limited.
The diameter of galvanized wire can vary from very thin (approximately 0.5 mm) to much thicker gauges (up to 10 mm or even larger), making it versatile across different fields. In addition to its robustness, galvanized wire maintains its ability to stretch and bend, allowing it to be shaped into various forms without losing its structural integrity.
Benefits of Galvanized Wire
1. Corrosion Resistance The primary advantage of galvanized wire over untreated wire is its ability to resist corrosion. The zinc coating acts as a sacrificial layer; it corrodes in place of the underlying metal, significantly prolonging the wire's lifespan.
2. Durability Galvanized wire can withstand harsh environmental conditions, including extreme temperatures and humidity, which makes it ideal for outdoor use. The protective zinc layer ensures that the wire maintains its integrity over time, thus requiring less frequent replacements.
3. Cost-Effectiveness Although the initial cost of galvanized wire may be higher than its non-galvanized counterpart, the long-term savings due to reduced maintenance and replacement costs make it a more economical choice in the long run.
4. Versatility Galvanized wire can be used in a variety of applications, from fencing and construction to arts and crafts. Its flexibility allows it to be utilized in different configurations while retaining strength.
5. Safety The use of galvanized wire, particularly in construction and agricultural applications, reduces the risk of accidents caused by rusting or frayed wires, which can be hazardous.
galvanized wire material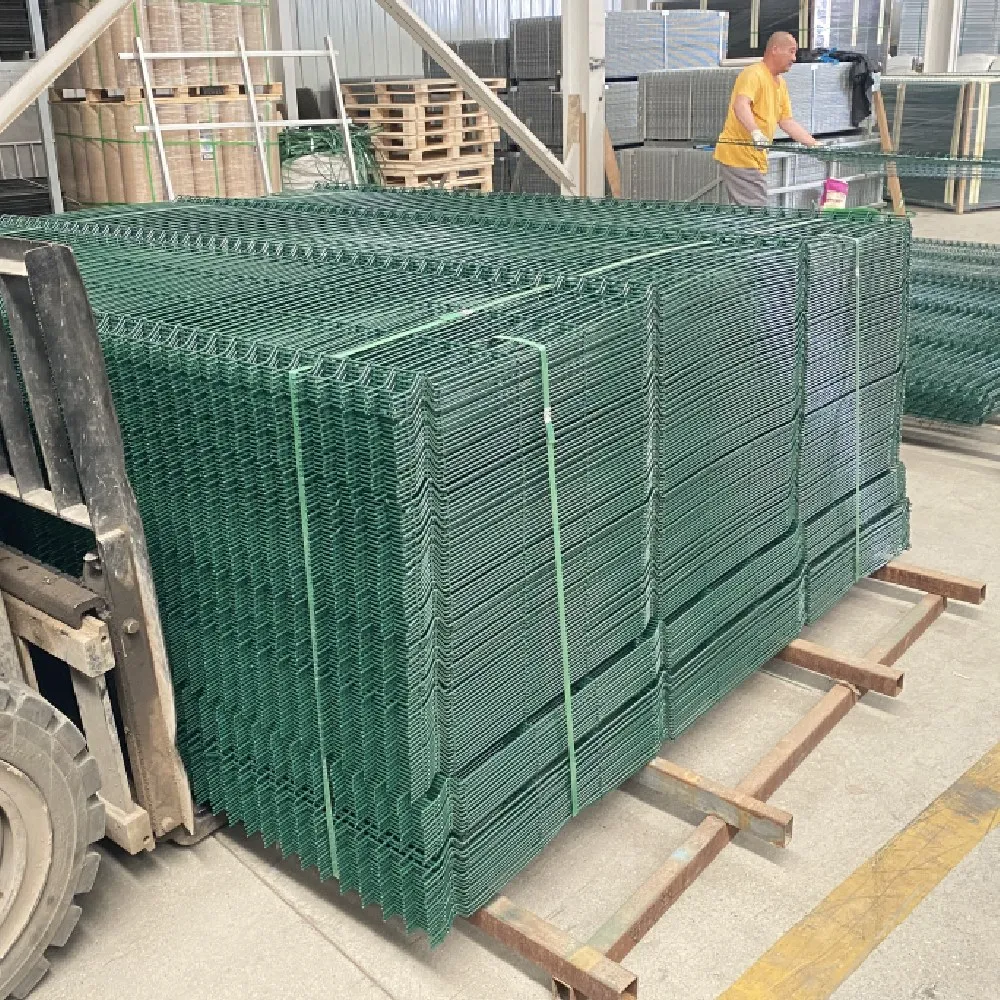
Applications of Galvanized Wire
Galvanized wire is used in a wide range of sectors, including
- Construction In building structures, galvanized wire is used for tying rebar, creating formwork, and reinforcing concrete, ensuring stability and longevity.
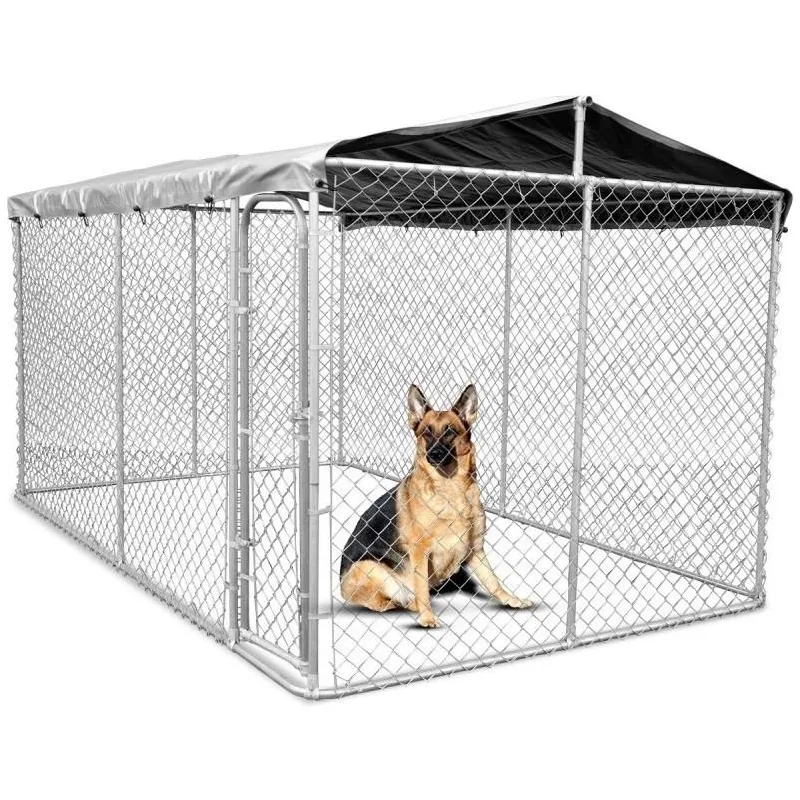
- Fencing Galvanized wire is commonly used to create durable and long-lasting fences for agricultural purposes, protecting livestock and crops from predators.
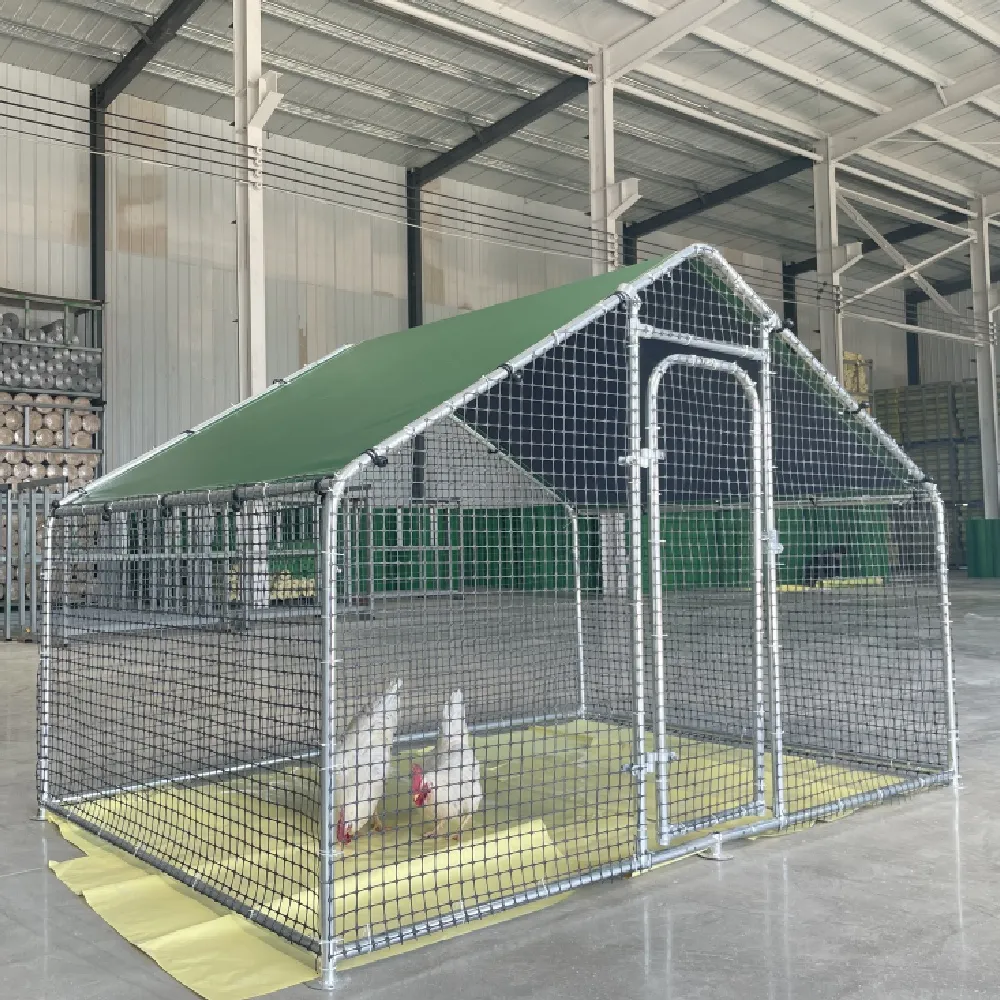
- Gardening and Horticulture It serves various functions in gardening, such as support for plants, trellising, and creating protective enclosures for tender plants.
- Manufacturing Galvanized wire is fundamental in manufacturing processes where strong yet malleable wire is needed, including the production of wire products, mesh, and nets.
Environmental Impact
The galvanization process can have environmental considerations, primarily due to the energy required and the potential for zinc waste. However, galvanized wire can contribute positively to environmental sustainability. Its long life cycle reduces the need for frequent replacements, which decreases waste. Moreover, zinc is a recyclable material, and many industries are implementing recycling processes for galvanized products to minimize environmental footprints.
Conclusion
Galvanized wire material serves as a cornerstone in modern construction, landscaping, and various industrial applications. Its unique properties, including exceptional corrosion resistance and durability, make it a sought-after choice across many sectors. Understanding the features and benefits of galvanized wire allows consumers and industry professionals alike to make informed decisions that lead to greater efficiency, sustainability, and safety in their projects. With its versatility and long-lasting nature, galvanized wire continues to be an indispensable asset in a world increasingly focused on durability and reliability.