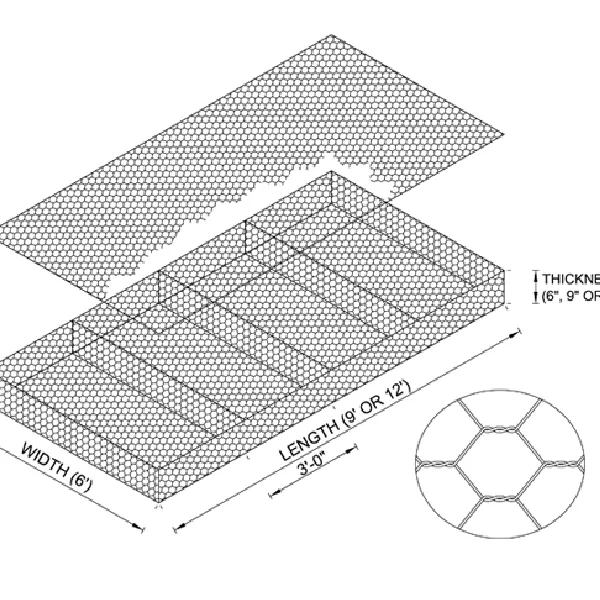
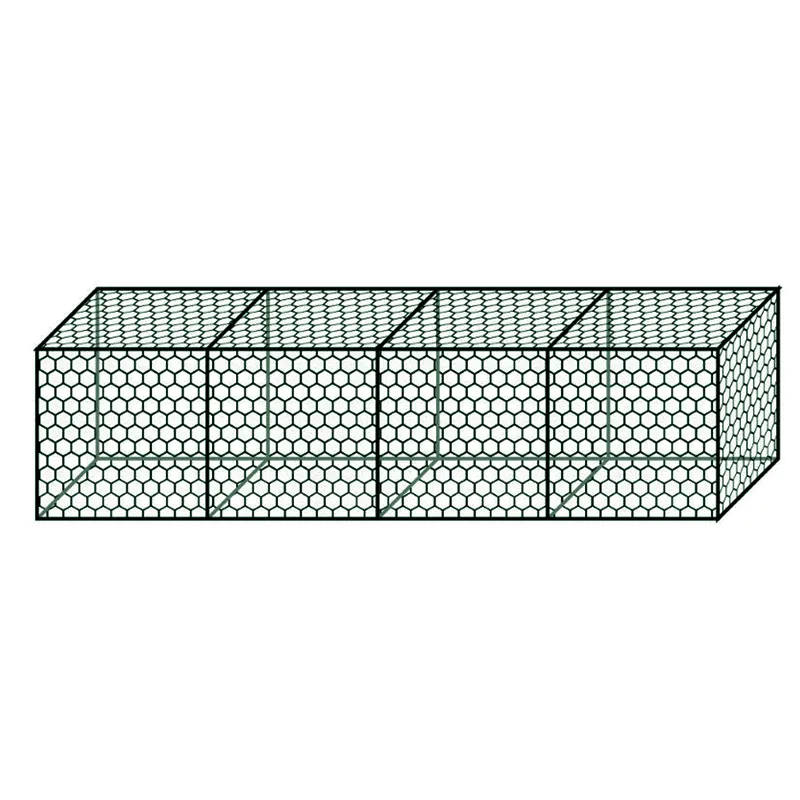
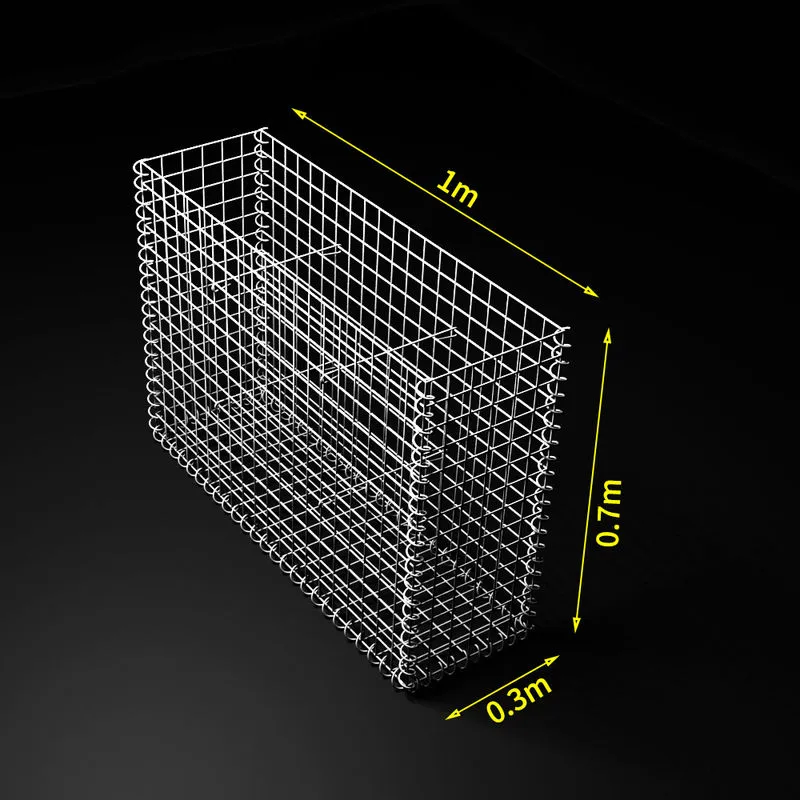
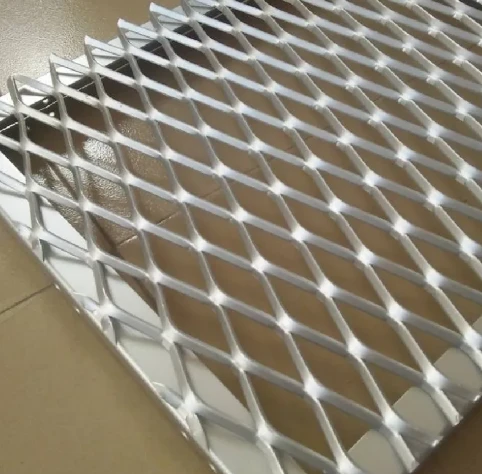
Thin metal meshes have become an indispensable component in a variety of applications across numerous industries due to their versatility, efficiency, and durability. As someone deeply familiar with the nuances of this product and its applications, I can discuss its multifaceted benefits and why it’s increasingly becoming a choice material for engineers, architects, and designers alike.
To start, thin metal meshes are prized for their strength-to-weight ratio. Unlike solid metal structures, these meshes maintain structural integrity while using significantly less material. This characteristic is especially advantageous in the automotive and aerospace industries, where weight reduction directly correlates with enhanced performance and fuel efficiency. In these sectors, every gram counts, and thin metal mesh delivers without compromising on strength or durability.
This material is also lauded for its exceptional thermal and electrical conductivity. Such properties make thin metal mesh ideal for use in electronics and heat dissipation applications. For instance, in electrical components, thin metal meshes can function as grounding grids, shielding against electromagnetic interference (EMI), and ensuring smooth electrical performance. Their thermal conductivity also makes them perfect as heat sinks or in components necessary for temperature regulation.
This is crucial in ensuring the longevity and reliability of modern electronic devices.

Moreover, thin metal meshes offer excellent filtration capabilities. In the realm of chemical processing and environmental engineering, they are used extensively to separate, filter, and purify liquids and gases. These meshes can be designed with varying apertures to trap specific particles, making them highly efficient and adaptable to different filtration needs. This adaptability is significant in water treatment facilities and air filtration systems where precision and reliability can impact both environmental and public health.
thin metal mesh
Architects and designers have also embraced thin metal mesh for its aesthetic and functional properties. In construction, these meshes are often employed in façades, sunshades, and interior decor to create visually appealing yet functional designs. The interplay of light and shadow that thin metal mesh facilitates not only enhances the aesthetic appeal of a structure but can also contribute to energy efficiency. By minimizing direct sunlight, these meshes help in cooling interiors, thereby reducing the reliance on air conditioning systems.
Equally important is the corrosion resistance of thin metal meshes. Being frequently exposed to the elements, especially in construction and marine applications, these meshes are crafted from materials like stainless steel or are coated to resist rust and degradation. This prolongs their service life and reduces the need for costly replacements or repairs, thus offering long-term financial benefits.
Furthermore, the production process of thin metal meshes has evolved dramatically, incorporating cutting-edge technologies that ensure precision and uniformity. Advanced techniques, such as laser cutting and chemical etching, allow for the creation of meshes with exacting specifications. This attention to detail is crucial in sectors where even the smallest deviation can lead to significant issues, such as aerospace engineering or medical device manufacturing.
In summary, thin metal meshes represent a confluence of innovation and practicality. Their extensive application across diverse sectors attests to their unparalleled utility. Whether it's creating lightweight components, ensuring efficient thermal and electrical performance, delivering reliable filtration, or enhancing aesthetic and structural designs, thin metal meshes continue to prove their worth. For those in the industry, understanding and leveraging the capabilities of this material is not just beneficial—it’s essential. By keeping abreast of the latest developments and applications of thin metal mesh, professionals can ensure they remain at the forefront of technological and industrial advances.