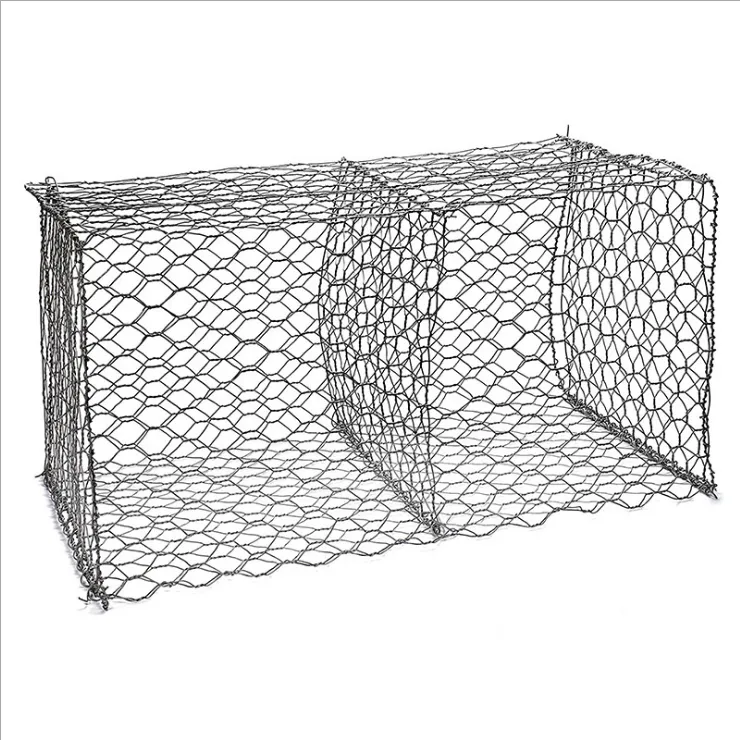
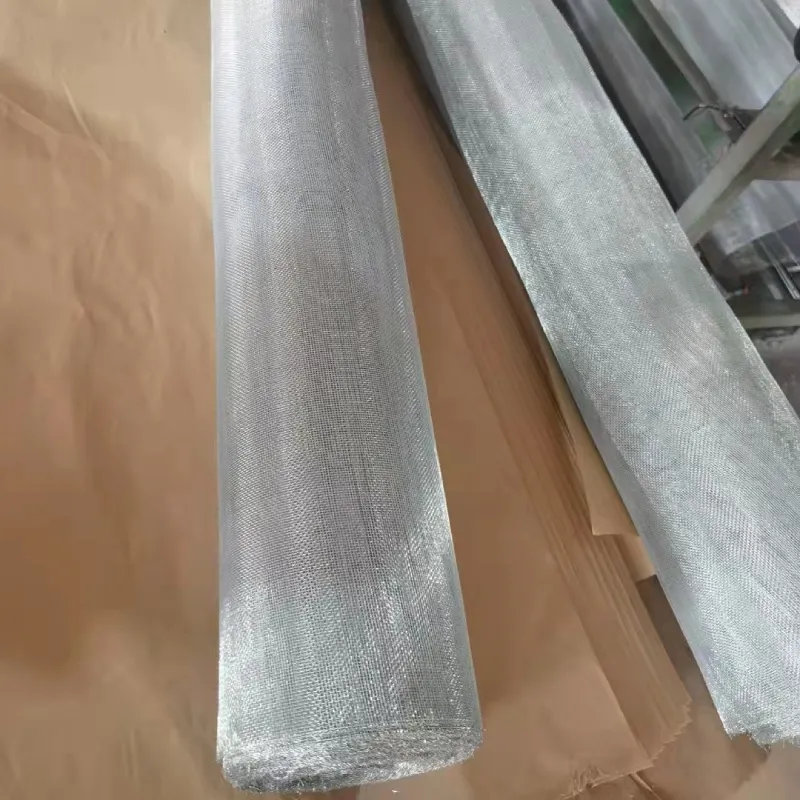
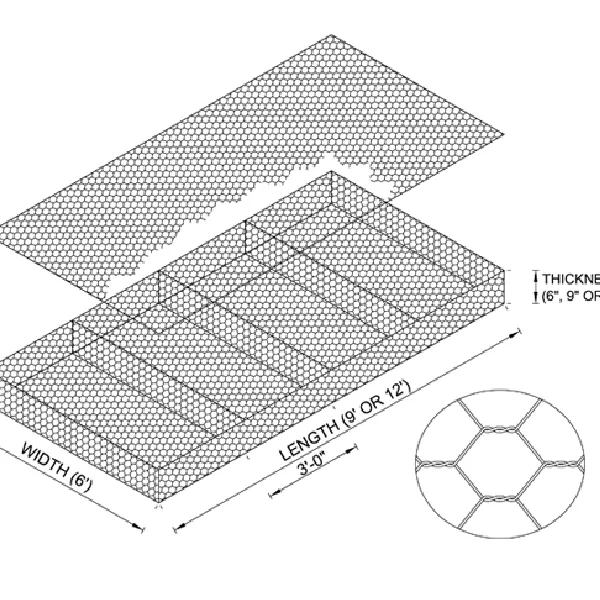
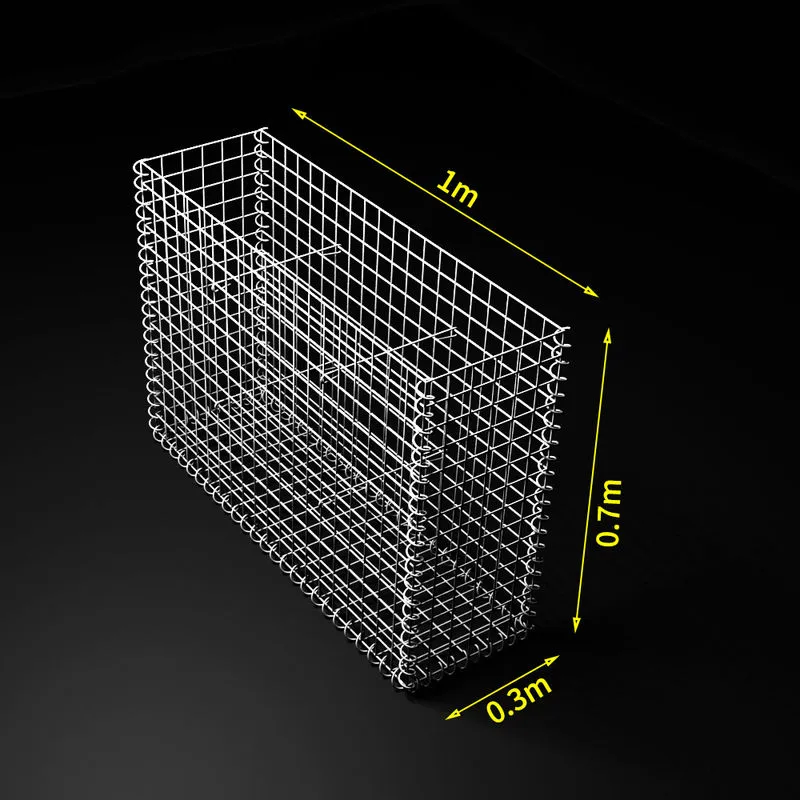
Gauge galvanized wire, a crucial component in both industrial and domestic applications, stands as a testament to the advancements in material technology. It is produced through a meticulous process of galvanization, where a protective zinc coating is applied to steel or iron wires to prevent rusting. This wire, available in various gauges, plays a pivotal role in construction, agriculture, and manufacturing due to its exceptional durability and versatility.
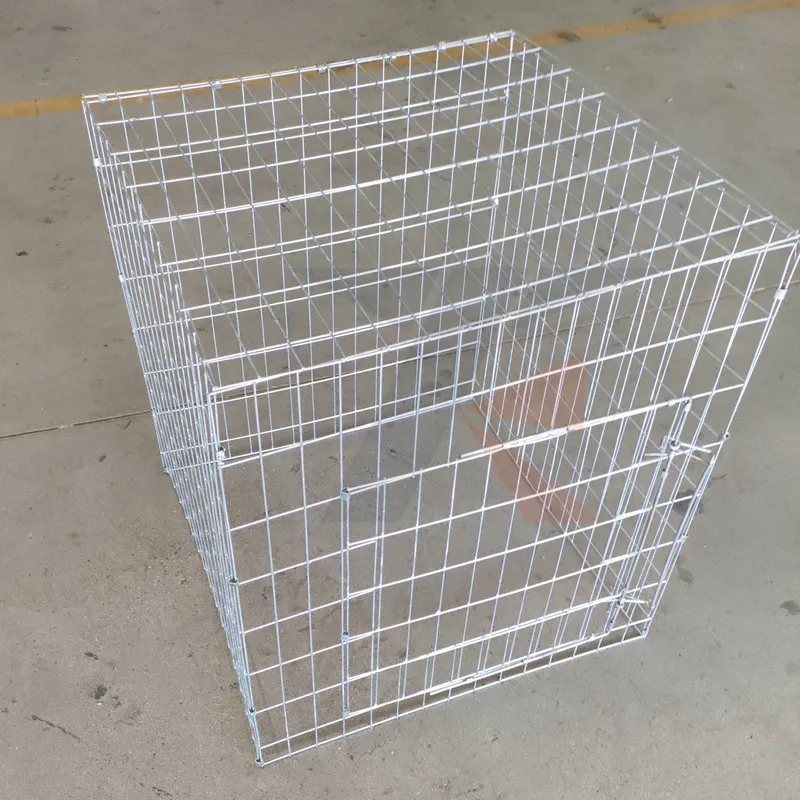

The production of gauge galvanized wire begins with selecting high-quality steel rods, ensuring the end product will meet rigorous standards. The rods undergo a deep cleansing process to remove impurities, followed by annealing, a heat treatment method that enhances the wire’s ductility. Post annealing, the wire is immersed in a molten zinc bath, a process known as hot-dip galvanizing. This technique ensures a robust and uniform coating that guards against corrosion.
The significance of gauge sizes in galvanized wire cannot be overstated. The gauge determines the wire's thickness, directly impacting its strength and application suitability. A lower gauge number signifies a thicker and more robust wire, ideal for tasks demanding greater strength, such as fencing in areas prone to severe weather. Conversely, higher gauge wire, being thinner, is suited for less demanding tasks, such as wiring in home decorations or light-duty binding.
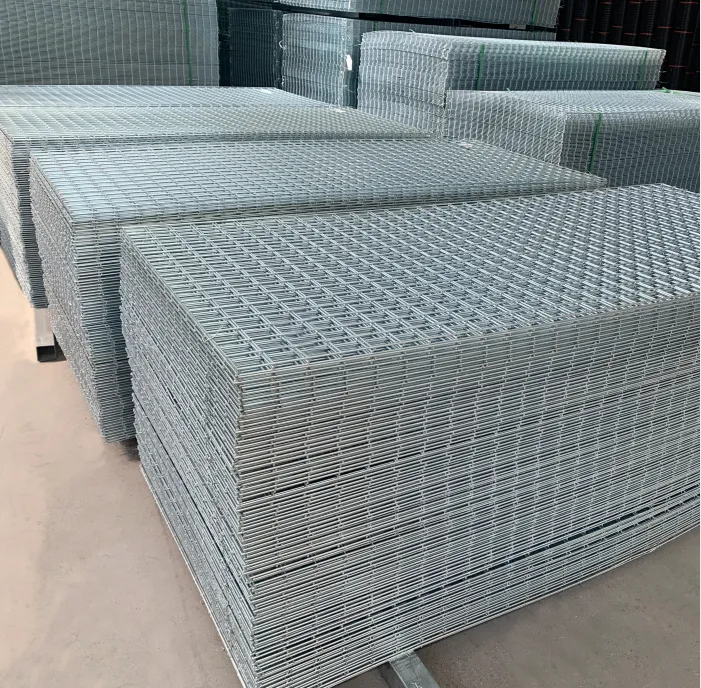

Industries benefit immensely from the unique properties of galvanized wire. In agriculture, it is indispensable for fencing, trellising in vineyards, and constructing animal enclosures due to its resistance to weather conditions and longevity. The construction sector employs this wire in reinforcing materials, binding, and even in scaffolding. Its reliability in preventing structural weaknesses makes it a preferred choice.
Special care must be taken when working with galvanized wire to maintain its integrity and strength. Experts suggest ensuring proper tension when installing the wire to prevent sagging or breaking. Additionally, using the appropriate tools for cutting and bending can minimize potential damage to the zinc coating, thereby prolonging the wire’s life span.
gauge galvanized wire
When selecting gauge galvanized wire, understanding environmental conditions is essential. Coastal areas, with high salt levels in the air, require heavily galvanized wire to resist accelerated corrosion rates. Similarly, industrial atmospheres, often laden with pollutants, necessitate wire with extra zinc coating for enhanced protection.
Trust in gauge galvanized wire stems from its proven track record in enhancing the longevity and safety of projects. Manufacturers often provide detailed specifications and certification upon purchase, underlining their commitment to quality. This transparency allows professionals to rely on the wire's capabilities and alignment with industry standards.
In terms of innovation, manufacturers continue to explore advanced galvanization techniques to further improve performance and sustainability. Such advancements include developing zinc-aluminum coatings, offering superior corrosion resistance and extending the wire's longevity even further in hostile environments.
Consumer feedback has consistently highlighted the wire's affordability and exceptional value, especially when considering its extended lifespan and minimal maintenance requirements. This feedback has led to increased demand, prompting suppliers to diversify their offerings across a broader range of gauges and conditions catering to specific needs.
Gauge galvanized wire epitomizes high standards of craftsmanship and technological progress. Its widespread acceptance and application across various sectors underscore its importance and reliability. By continually advancing production processes and maintaining stringent quality controls, the industry ensures that galvanized wire remains a cornerstone in modern infrastructure and agriculture development.