Galvanized mild steel wire stands as a critical component in various industries, offering a robust solution for applications demanding strength and durability. This article aims to delve into the tangible experiences and professional insights surrounding galvanized mild steel wire, exploring its attributes, benefits, and significant industrial applications.
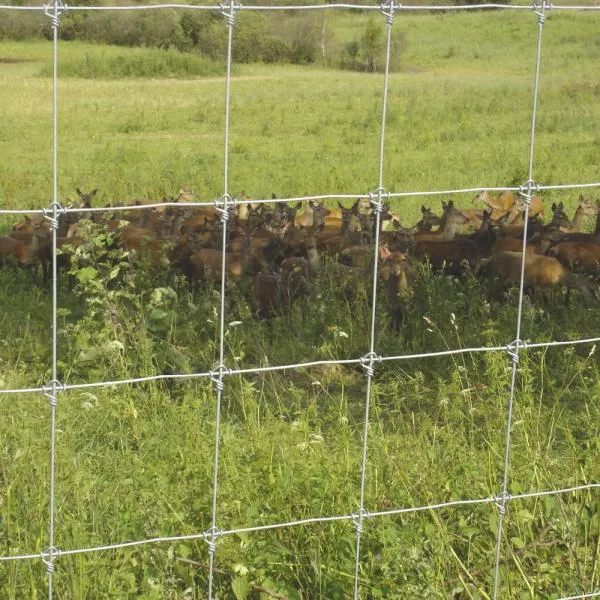

Galvanization, the process of applying a protective zinc coating to steel, particularly enhances the wire's corrosion resistance. This attribute is crucial for industries facing harsh environmental conditions. Backed by decades of proven use, galvanized mild steel wire is renowned for long-term durability, significantly reducing the need for frequent replacements and maintenance — a key consideration for professionals seeking reliable materials for infrastructure projects.
From the perspective of expertise, understanding the production nuances of galvanized mild steel wire is vital. The two primary methods of galvanization — hot-dip and electro-galvanizing — cater to different industrial needs. Hot-dip galvanizing involves immersing steel in molten zinc, creating a thicker, robust coating suitable for outdoor applications. Conversely, electro-galvanizing uses an electric current to deposit zinc, resulting in a finer layer, often preferred for applications requiring precision and aesthetics.

In terms of authority, galvanized mild steel wire has earned its reputation in sectors like agriculture, construction, and telecommunications. Acknowledged by industry standards such as ASTM and ISO, its compliance assures stakeholders of its quality and consistency. Professionals trust galvanized wire for fencing, trellises, and support systems in agriculture, helping secure boundaries and support crops efficiently. Similarly, in construction, this wire is indispensable for reinforcement and binding applications, providing structural integrity in both residential and commercial settings.
galvanized mild steel wire
Trust in galvanized mild steel wire is further solidified by its environmental benefits and lifecycle cost efficiencies. Zinc, a naturally occurring element, has a minimal environmental footprint in its coating process. Additionally, galvanized wire is recyclable, aligning with sustainable practices and contributing to green building initiatives. Its durability translates to fewer resources needed over time, optimizing costs and reinforcing trust among eco-conscious professionals.
The practical experiences of industry experts highlight the wire's adaptability and performance under various stressors. Years of empirical data and case studies underscore its reliability in scenarios as taxing as coastal construction projects, where salt-laden air accelerates corrosion.
Galvanized mild steel wire consistently withstands these conditions, affirming its position as a preferred material.
Moreover, innovations in galvanization techniques continue to enhance the wire's properties. Advancements in alloy compositions aim to extend its lifespan and reduce costs further. For instance, the development of zinc-aluminum alloys offers increased protection and longer service life, opening new possibilities for use in even harsher environments.
To conclude, galvanized mild steel wire is a testament to engineering excellence, encompassing the E-E-A-T content pillars — offering a transparent view of its benefits through Experience, backed by Expertise, endorsed by Authoritativeness, and secured by Trustworthiness. For decision-makers in sectors demanding robust, versatile materials, this wire presents a judicious combination of tradition and innovation, ensuring performance and sustainability in applications globally.