Understanding what a gabion box is and its applications requires diving into the realms of civil engineering, landscaping, and environmental preservation. As constructs known for their versatility and robust nature, gabion boxes have gained traction in both industrial and domestic settings. Used widely from stabilizing shorelines to crafting stunning garden terraces, gabion boxes are a fascinating blend of traditional building techniques and modern engineering sophistication.
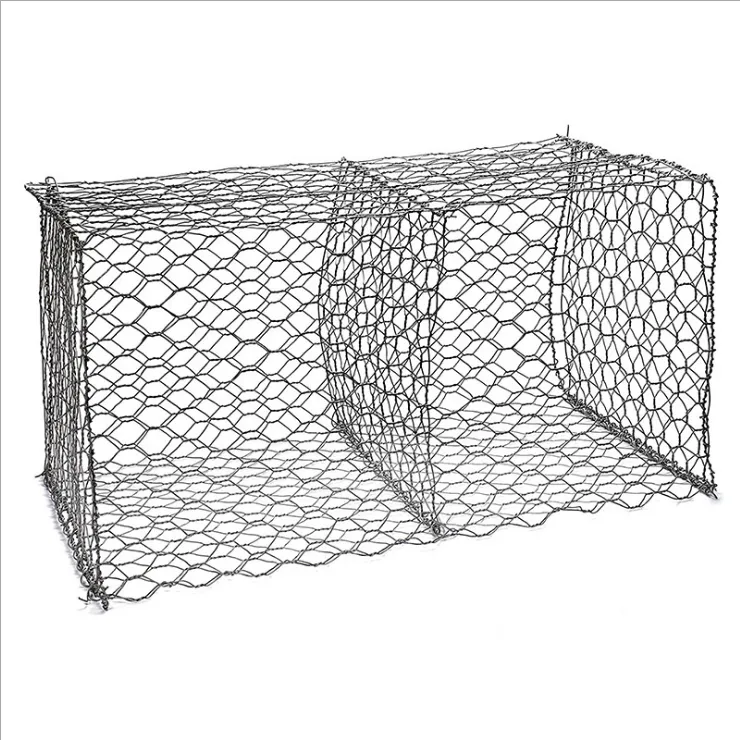
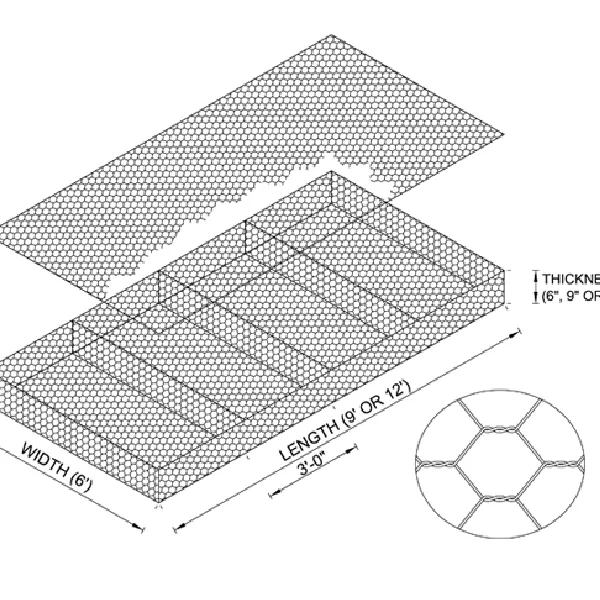
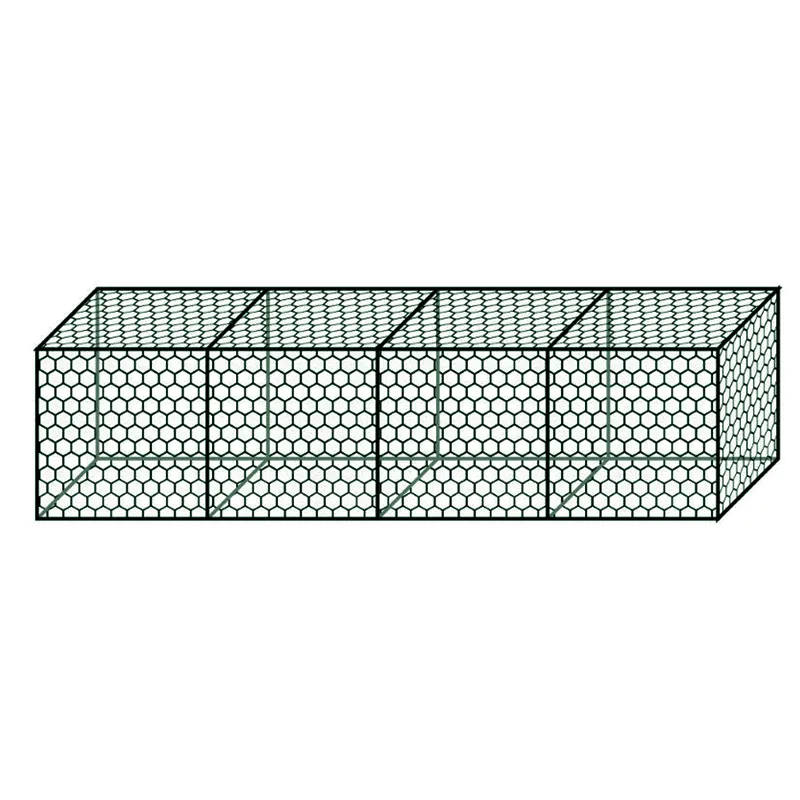
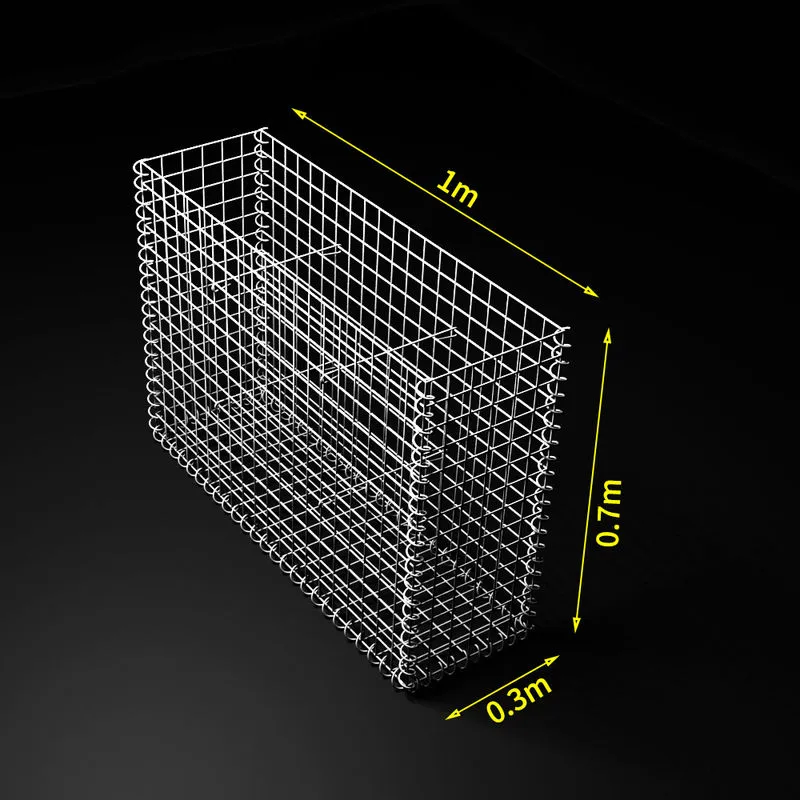
A gabion box is essentially a cage constructed of wire or mesh that is filled with stones, concrete, or occasionally soil. Its name originates from the Italian word “gabbione,” meaning “big cage.” These simple yet effective structures are utilized primarily in civil engineering and landscaping projects. Their adaptation is attributed to several practical attributes durability, permeability, and eco-friendliness.
From an engineering perspective, gabion boxes offer significant advantages due to their flexibility and resilience under pressure, making them ideal for erosion control and bank stabilization. When water levels rise and fall, their semi-flexible structure allows for minimal damage, unlike rigid concrete constructions. The granular nature of their fill allows water to filter through, relieving hydrostatic pressure and reducing the risk of wall failure.

The expertise of engineers is pivotal in tailoring gabion box installations for specific environments. Installation often requires geological surveys and careful planning to ensure the structure aligns with the natural movement of water and soil. The placement of a gabion box must consider local topography and hydrology to maximize its stability and effectiveness.
In landscaping, gabion boxes have emerged as both functional and aesthetic elements. Whether used to create terraces that combat soil erosion or as decorative walls that blend seamlessly into natural surroundings, their rustic charm and modularity make them a popular choice. The expertise of landscapers in selecting stone types and arrangement within the gabion can significantly influence the overall visual impact and durability, offering a unique blend of art and functionality.
what is a gabion box
Authorities in the construction and environmental management fields often endorse gabion boxes for their minimal environmental impact. Made from natural materials, they integrate into habitats without significant ecological disruption. Moreover, they promote ecological colonization—the spaces between stones provide niches for plant growth and small wildlife, enhancing biodiversity.
Trust in gabion boxes as sustainable infrastructure solutions is further bolstered by their long track record. These structures have been used since ancient times, yet their basic principles remain highly applicable in modern construction. Modern gabion construction often utilizes high-quality galvanized or PVC-coated wire to increase longevity and performance, especially in harsh environments.
For homeowners and small-scale projects, the approachability of gabion boxes as DIY projects is another trust factor. Their straightforward assembly and lack of necessity for advanced tools make them accessible to hobbyists seeking to enhance their landscapes.
In recent years, gabion boxes have seen an expansion in use beyond traditional applications. Urban planners now consider them for integrating green spaces into built environments, recognizing their potential in diverting stormwater, reducing urban heat, and providing green corridors.
In conclusion, whether applied in major civil projects or small garden installations, gabion boxes symbolize a perfect marriage of age-old techniques and contemporary engineering knowledge. Their adaptability, economic efficiency, and environmental credentials make them a compelling choice in an era increasingly focused on sustainable development. As experts perpetually refine materials and methodologies, gabion boxes seem poised to continue their legacy as stalwarts of both preservation and innovation in the built environment.