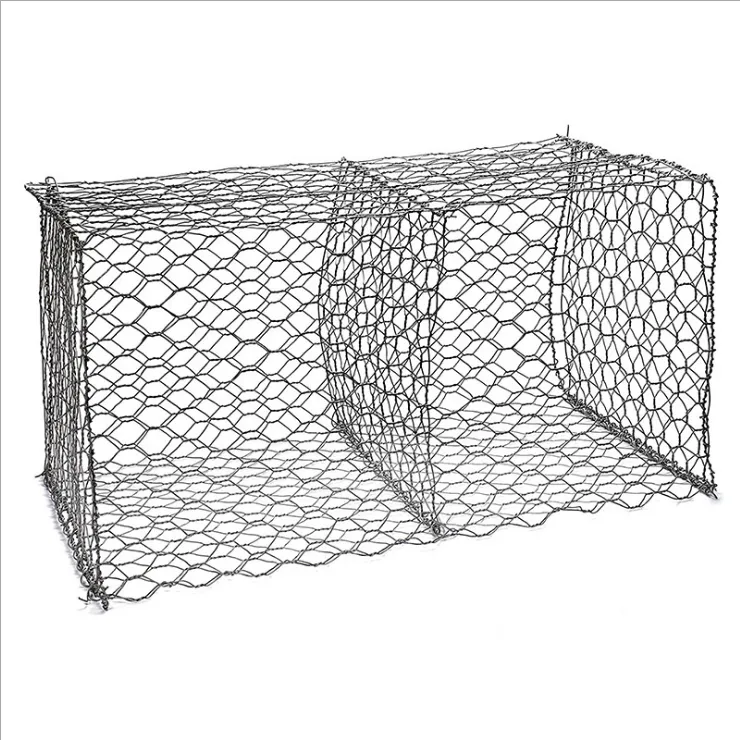
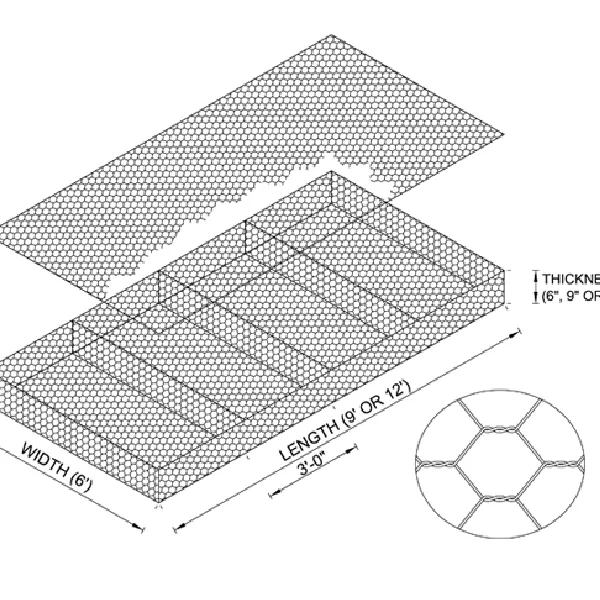
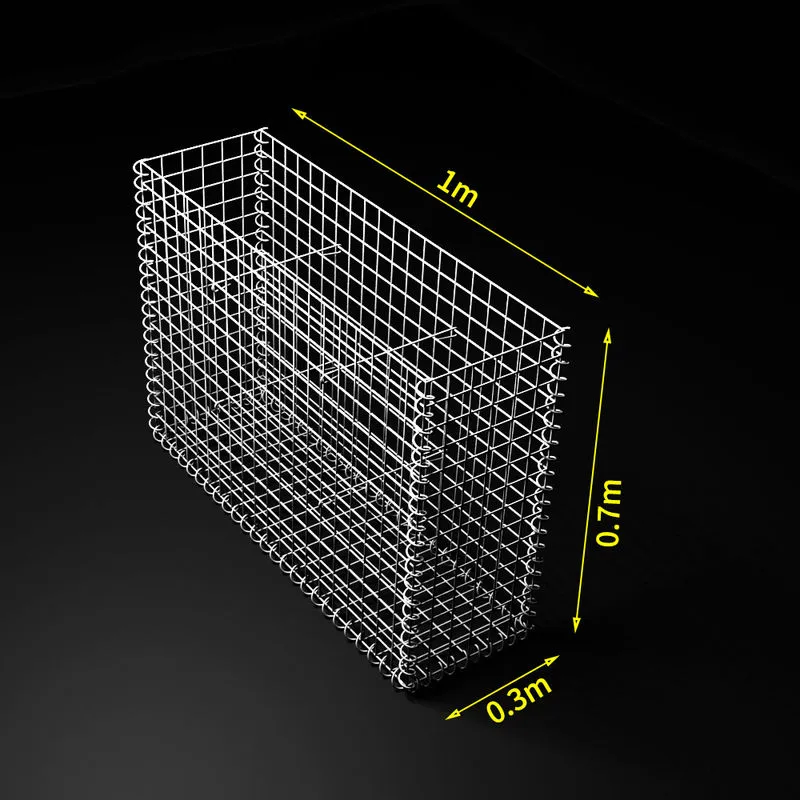
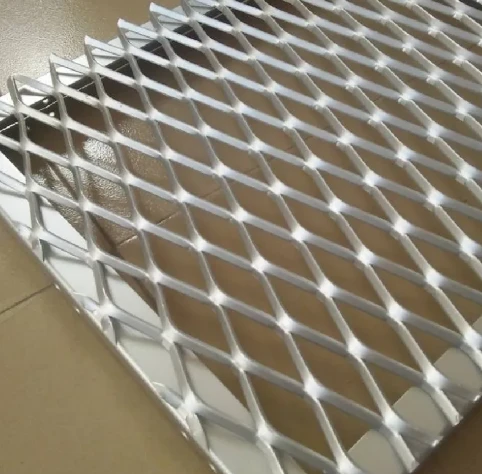
Extruded metal mesh, often revered for its versatility and robustness, plays an instrumental role in various industrial and architectural applications. This unique type of metal mesh is crafted through an extrusion process, a method where the metal material is forced through a mesh die to create long strands or sheets with desired patterns. The resulting product is not only robust and durable but also offers a plethora of customization options. Reflecting deeply on its multifaceted applications, this article aims to delve into the authentic experiences, professional insights, authoritative recommendations, and trustworthy validations surrounding extruded metal mesh.
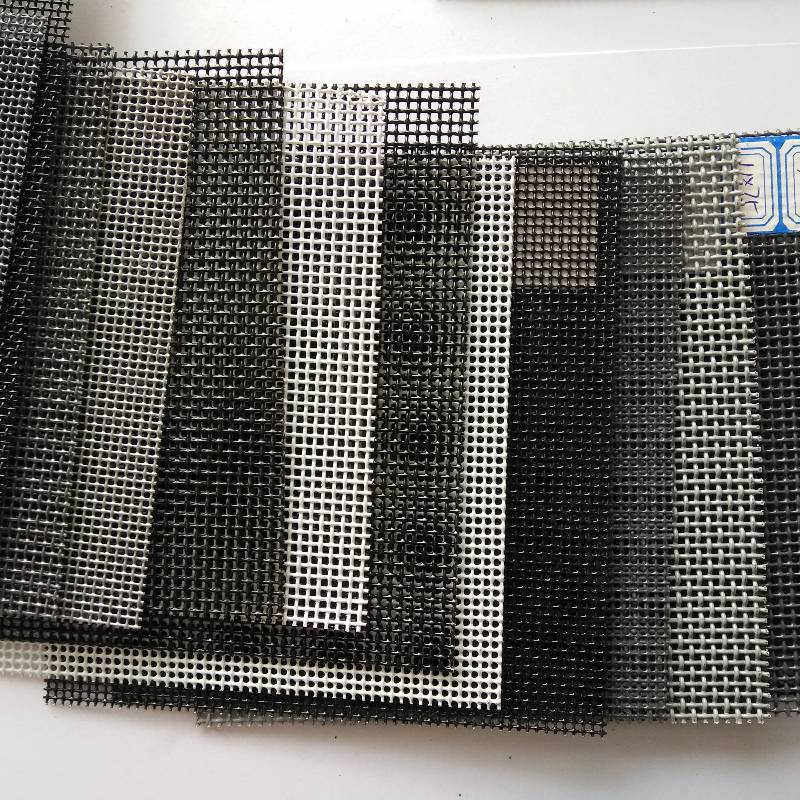

In-depth understanding reveals extruded metal mesh's unparalleled flexibility, which makes it an indispensable asset in sectors like construction, automotive, aerospace, and even interior design. Experienced engineers and architects often cite their reliance on extruded metal mesh for projects that demand high strength-to-weight ratios. The mesh's configuration can be easily tailored to meet specific requirements, providing enhanced load-bearing capacity while minimizing material weight—a unique combination that is rare in traditional construction materials.
Expertise in utilizing extruded metal mesh continues to grow, given its superior qualities. Professionals with substantial experience in metallurgical engineering advocate for its use due to its resistance to corrosion and extreme temperature variations. This mesh type easily withstands the harsh conditions found in outdoor architectural structures or high-temperature environments in industrial applications. For example, in the automotive industry, it's commonly utilized for grilles and protective barriers, showcasing its impeccable ability to combine functionality with aesthetic appeal.
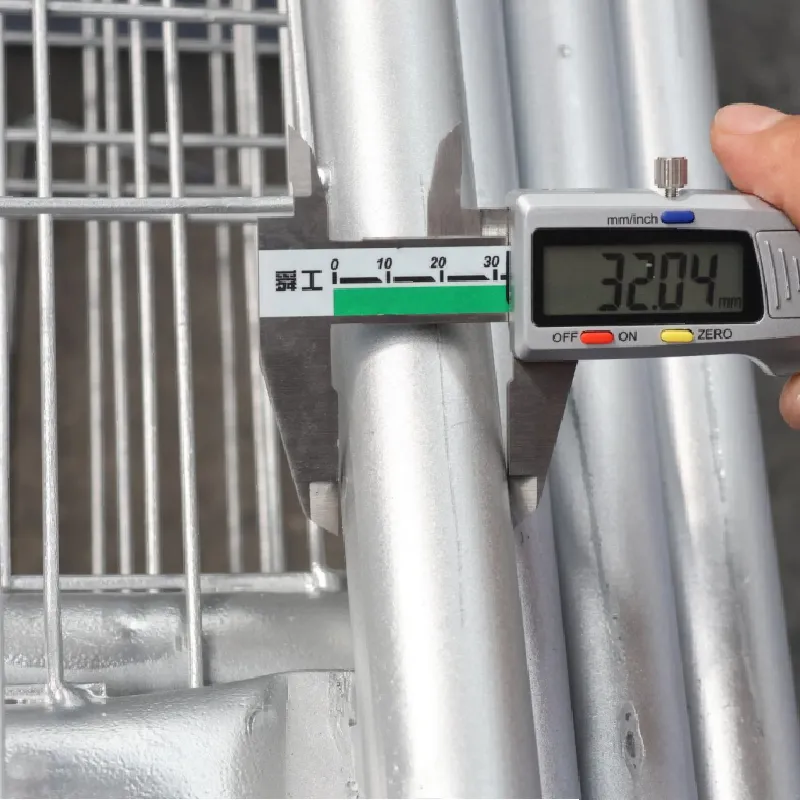

Authority figures in the industry, such as leading construction firms and certified metallurgical specialists, often defer to extruded metal mesh when discussing sustainable and innovative building practices. Its production process generates considerably less waste compared to other mesh types, aligning with global sustainability goals. Additionally, its durability translates into longer life spans for the products it is used in, reducing the environmental impact associated with frequent replacements.
extruded metal mesh
Trustworthiness of extruded metal mesh is solidified by numerous satisfied testimonials from businesses that have integrated it into their operations. Case studies and detailed reviews occasionally highlight the mesh's dependability, focusing on its consistent performance and reliability under stress. Companies have reported decreased long-term maintenance costs and improvements in overall product lifetime upon opting for extruded metal mesh solutions.
Navigating the purchasing decisions for extruded metal mesh involves evaluating specific project requirements, as this ensures the selection of the optimal mesh pattern and material composition. Professionals skilled in materials science recommend considering the operational environment's demands, such as exposure to chemicals, mechanical stress, or thermal conditions, to maximize the mesh's effectiveness.
The future of extruded metal mesh lies in continued innovation and technological advancements in the field. Researchers explore new alloys and composite materials to enhance its properties further, aiming to unlock even more applications. Breakthroughs in extrusion technology are anticipated to refine the precision of mesh patterns, opening up possibilities for increased customization and performance capabilities.
In summary, extruded metal mesh stands as a testament to engineering excellence, offering an array of benefits that cater to a variety of industrial needs. Its adaptability and resilience remain unmatched, providing a trustworthy option for professionals who strive for both efficiency and sustainability. As its applications continue to expand, the legacy of extruded metal mesh is set to perpetuate, fostering advancements and setting new benchmarks in material science.